

While no objects make it to Gen1 or Gen2 a GC cycle occurs about every 20 seconds. The aim of this test is to ensure acceptable memory pressure and GC cycles on the server instance in a controlled usage scenario and ensure no memory leaks occur.Įxecution is consistant. When the test completes, the server returns to a steady state of memory usage prior to the test beginning. Given the artificial environment restrictions this imposes its difficult to pin down exact KPIs but in general this test is used to monitor: MetricĮxpect to see steady Gen0 allocation over time, with no extreme spikes.Įxpect to see little to no objects surviving to Gen1 and Gen2 heap collections per GC cycle. Each user executes a query every 0-15ms until failureĪ qualitative test executed with the server instance running in release mode, harnessed via dotMemory.Starts 20 new users each second until failure.JMeter script: graphql-max-load-generator.jmx.

This workload acts as a control to compare performance of the baseline web api against the overhead of the graphql library.Each user executes 10,000 requests at most 15ms apart.300 concurrent users executing a REST Query that mutates and returns a single object.300 concurrent users executing a REST Query that fetches a single object.2 registered subscription per client (1000 total client subscriptions).A custom console app that registers subscribers to receive subscription events generated via the Load Generating Workstation mutations.300 concurrent users executing a graphql mutation (and raising a subscription event).300 concurrent users executing a graphql query to fetch a single object.JMeter script: graphql-load-generator.jmx.Each user executes 10,000 requests at most 30ms apart.15 concurrent users executing a graphql query to fetch a single object.JMeter script: graphql-memory-profiling.jmx.Simple queries to fetch or mutate a single, in-memory object.Garbage collection executing in server mode.src/ancillary-projects/benchmarking/graphql-aspnet-load-server/ These tests are executed in a controlled setting with the following conditions: Test Configuration and Specs GraphQL ASP.NET Server: Our goal is to measure the theoretical limits in a multi-user, "production like" scenario. We periodically execute tests against the library to measure throughput and stability, for a single server instance, under load. Be sure to execute your own load tests using queries indicative of your expected user base and act accordingly. database connections, service orchrestration, business logic etc.). Your use cases will be different and effected by factors not present in our lab environment (e.g. These performance tests are not intended to be used as data points when determining scaling requirements for your own production workloads. If there is a specific query type or scenario that you are seeing a significant performance degregation with please open an issue on github and let us know! Obviously, real world workloads are going to be slower than these theoretical values, but the faster we can make the benchmarks the faster all other scenarios will be.Īs you can see all query types execute in sub-millisecond timeframes.
#Graphql vs rest performance code
The goal of our benchmarks is to measure the library's abiliy to process a query in isolation, to perform the query and execute user code not how long an action method takes to query a database for data and send a request over the wire. These are executed against an in-memory data store without an attached database. For our benchmarks, we are tracking a number of query types which measure performance via the various paths through the library multi controller queries, queries with variables etc. With that being said though, bottlenecks are rarely the language being used.Benchmarks & Performance Query Benchmarking Both outperform a Node gateway by significant margins. Now, depending on use-case, we will use Go ( ) or Rust ( ). Admittedly, we did use Node (Apollo) though up until about two years ago. We found Node in general to be incredibly slow, not to mention single threaded.
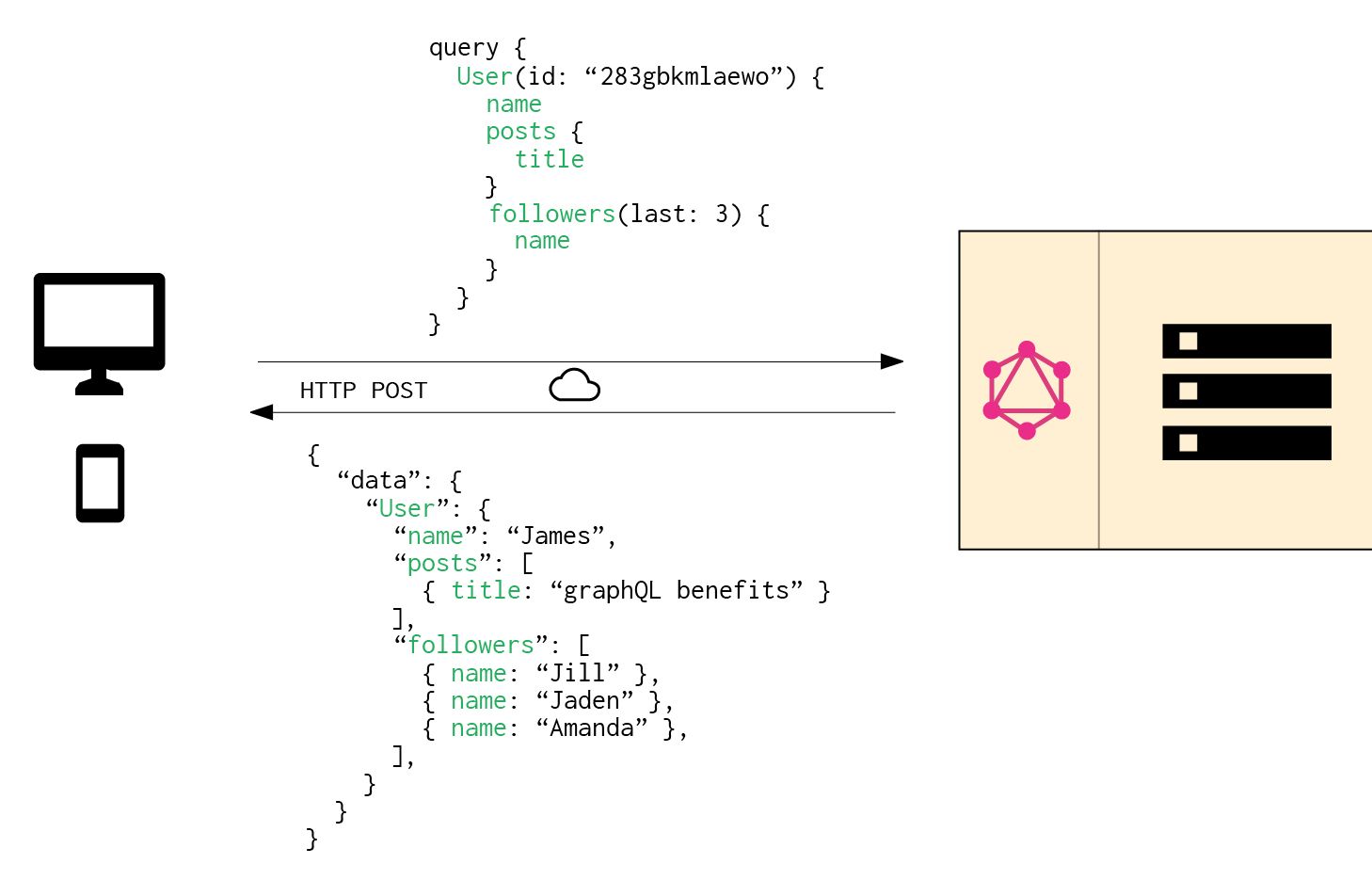
gRPC is much more performant than JSON RPC. The architecture we use today is a GraphQL gateway(s) that resolve to services via gRPC. That’s not meant as an insult just an observation. I feel like you’re not fully understanding the technology here. REST would take many trips to fetch all the data. For example, you could get a list of users, their addresses, friends, friends addresses, etc all in a single query. GraphQL resolves a request and depending on the data graph, a query might resolve after hitting multiple services and/or databases. I’ve been heavily using GraphQL since 2015.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
